Overview
Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) is essential for DNA synthesis, red blood cell formation, neurological function, and homocysteine metabolism. Deficiency can lead to megaloblastic anemia, neurological impairments, and elevated homocysteine levels, a potential risk factor for cardiovascular and cognitive disorders. High-dose oral vitamin B12 (1000 μg daily) has been shown to be effective in normalizing serum B12 levels in deficient individuals, with efficacy comparable to intramuscular administration, supporting its use even in those with malabsorption issues [1]. Supplementation significantly reduces plasma homocysteine concentrations, particularly in individuals with baseline deficiency, as confirmed by a meta-analysis of 21 RCTs [5]. However, despite its homocysteine-lowering effects, clinical trials have not consistently demonstrated benefits of B12 supplementation—alone or in combination with folic acid and B6—on cardiovascular events, cognitive decline, or depressive symptoms in high-risk populations [3][6][2].
Dosage Guide
Recommended Daily Allowance
For generally healthy individuals
Therapeutic Doses
For treatment of specific conditions
Special Forms
Alternative forms for specific needs
Preferred form in neurological conditions; active cofactor in methylation
Often used in injections; longer half-life and detoxification support
Common synthetic form in supplements; requires conversion in liver
Clinical Notes
- High-dose oral B12 (1000 mcg/day) is effective even in malabsorption states due to passive diffusion of small fraction (1% of dose).
- Neurological damage from B12 deficiency can be irreversible if untreated; early supplementation is critical.
- Monitor serum B12, methylmalonic acid (MMA), and homocysteine levels in suspected deficiency for accurate diagnosis.
- No established Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL) for B12 due to low toxicity, even at high doses.
Research
Daily oral B12 (1000 μg) is as effective as intramuscular B12 in normalizing serum B12 levels in deficient patients.
Systematic review found no evidence that B12 supplementation improves cognitive function in randomized trials.
Supplementation with B12, folic acid, and B6 did not reduce cardiovascular events or mortality in high-risk women.
Mixed B-vitamin supplements, including B12, reduce total homocysteine levels in acutely ill older patients.
Meta-analysis shows B12 supplementation significantly lowers homocysteine levels, especially in deficient individuals.
Homocysteine-lowering with B vitamins does not reduce cardiovascular events in people with or without pre-existing CVD.
Combination of omega-3, folic acid, and B vitamins is more effective at lowering homocysteine than omega-3 alone.
Adding B12, B6, and folic acid to antidepressant treatment did not significantly improve depressive symptoms in older adults.
Products Containing Vitamin B12(6 reports)

Ortho B Complex is a high-potency B-complex supplement delivering 50 mg each of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, and B6, along with 200 mcg B12, 1,360 mcg folic acid (B9), 75 mcg biotin, 19 mg choline, and 50 mg inositol. The formulation emphasizes pharmacological doses of B vitamins, particularly those involved in energy metabolism, homocysteine regulation, and neurological function.

BioActive Complete B-Complex is a high-potency B-vitamin supplement designed to support energy metabolism, neurological function, and homocysteine regulation. The formulation features all eight B vitamins at doses that meet or exceed clinically studied levels for key indications, with particular emphasis on B1, B2, B3, B6, B9, and B12 for metabolic and neurological support.
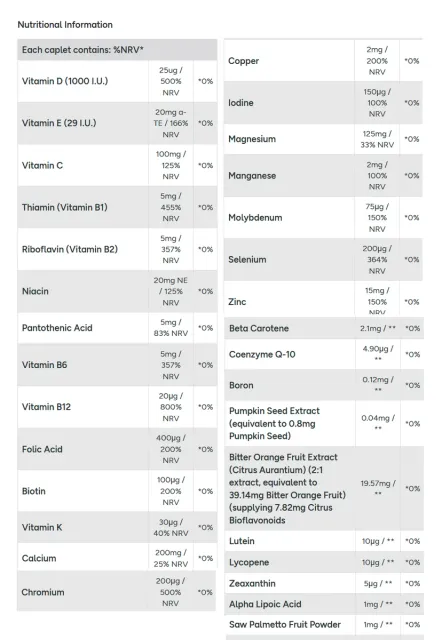
This supplement delivers high-dose vitamin D (25µg/1000 IU) as a primary ingredient, supported by a full B-complex, vitamins C and E. The formulation is designed to support immune function, metabolic health, and antioxidant defense, with clinically relevant dosing of key micronutrients.

HYDROXYCUT HARDCORE LIQUID HEAT is a thermogenic weight management supplement with caffeine and cayenne pepper extract as its primary active ingredients. These compounds are clinically shown to enhance metabolic rate, reduce energy intake, and support fat oxidation. The formulation includes supporting doses of B-vitamins and green coffee bean extract to complement energy metabolism and cardiovascular health.
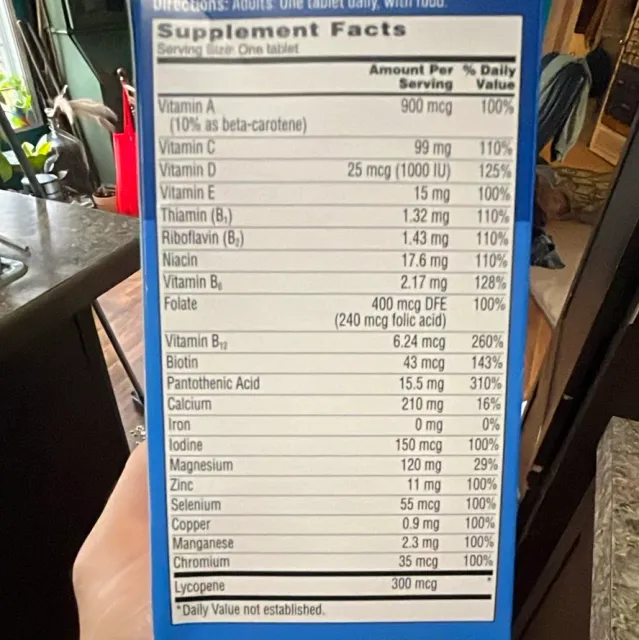
This multivitamin provides a comprehensive blend of essential vitamins at doses aligned with recommended dietary allowances and evidence-based clinical ranges. Vitamin D, B12, and folate are included at levels shown to support immune, neurological, and cardiovascular health, particularly in at-risk populations.

This supplement delivers apple cider vinegar (ACV) as its primary active ingredient, standardized to 1000 mg per serving, alongside supporting nutrients vitamin B12 and a small amount of sodium. The formulation is designed for metabolic and general wellness support, leveraging acetic acid and polyphenols from fermented apple cider. While the ACV dose aligns with common therapeutic intakes, the gummy format may delay acetate absorption compared to liquid forms.