Overview
Vitamin B9, also known as folate or folic acid, is essential for DNA synthesis, repair, and methylation, as well as red blood cell formation and homocysteine metabolism. It plays a critical role in fetal neural tube development, making adequate intake crucial during pregnancy to prevent neural tube defects (NTDs). Folic acid supplementation effectively reduces homocysteine levels, a biomarker associated with cardiovascular disease and cognitive decline, although clinical trials have not consistently demonstrated reductions in cardiovascular events or cognitive improvement [2][3]. Long-term supplementation with folic acid and other B vitamins has not shown significant benefits in preventing depression in older women or improving cognitive function in randomized trials, though some observational data suggest potential benefits in specific populations [1][7]. A trial in female migraine with aura patients found that 1 mg folic acid did not significantly reduce homocysteine or migraine frequency, highlighting variability in response [6].
Dosage Guide
Recommended Daily Allowance
For generally healthy individuals
Therapeutic Doses
For treatment of specific conditions
Upper Intake Limit
Maximum safe daily intake
1000 mcg— Applies to synthetic folic acid only, not food folate
Special Forms
Alternative forms for specific needs
For MTHFR polymorphisms, depression adjunct, folate metabolism issues
Methotrexate rescue, chemotherapy, metabolic disorders
Clinical Notes
- Rule out B12 deficiency before treating anemia - folate can mask B12 deficiency while neurological damage progresses
- High doses may mask B12 deficiency symptoms
- Prescription doses above UL require medical supervision
Research
Systematic review found no clear evidence that folic acid supplementation improves cognitive function in randomized trials.
Folic acid, B6, and B12 supplementation did not reduce cardiovascular events or total mortality in high-risk women.
Homocysteine-lowering with B vitamins, including folic acid, does not reduce cardiovascular events in people with or without pre-existing CVD.
Mixed B vitamin supplements, including folic acid, significantly reduce plasma homocysteine levels in acutely ill older patients.
Supplementation with B vitamins, including folic acid, effectively lowers homocysteine and increases blood vitamin levels, with no major differences between natural and synthetic complexes.
1 mg folic acid daily did not significantly reduce homocysteine or migraine frequency in women with migraine with aura.
Long-term folic acid (2.5 mg/day) and B vitamin supplementation did not reduce risk of depression in older women.
Not directly relevant to B9; focused on B12 supplementation and cobalamin levels.
Products Containing Vitamin B9(4 reports)

Ortho B Complex is a high-potency B-complex supplement delivering 50 mg each of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, and B6, along with 200 mcg B12, 1,360 mcg folic acid (B9), 75 mcg biotin, 19 mg choline, and 50 mg inositol. The formulation emphasizes pharmacological doses of B vitamins, particularly those involved in energy metabolism, homocysteine regulation, and neurological function.

BioActive Complete B-Complex is a high-potency B-vitamin supplement designed to support energy metabolism, neurological function, and homocysteine regulation. The formulation features all eight B vitamins at doses that meet or exceed clinically studied levels for key indications, with particular emphasis on B1, B2, B3, B6, B9, and B12 for metabolic and neurological support.
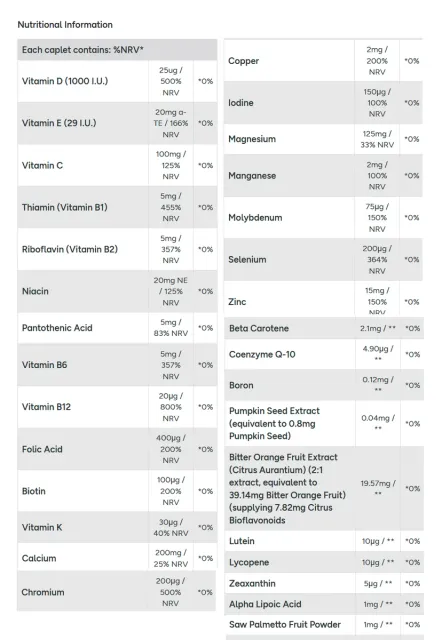
This supplement delivers high-dose vitamin D (25µg/1000 IU) as a primary ingredient, supported by a full B-complex, vitamins C and E. The formulation is designed to support immune function, metabolic health, and antioxidant defense, with clinically relevant dosing of key micronutrients.
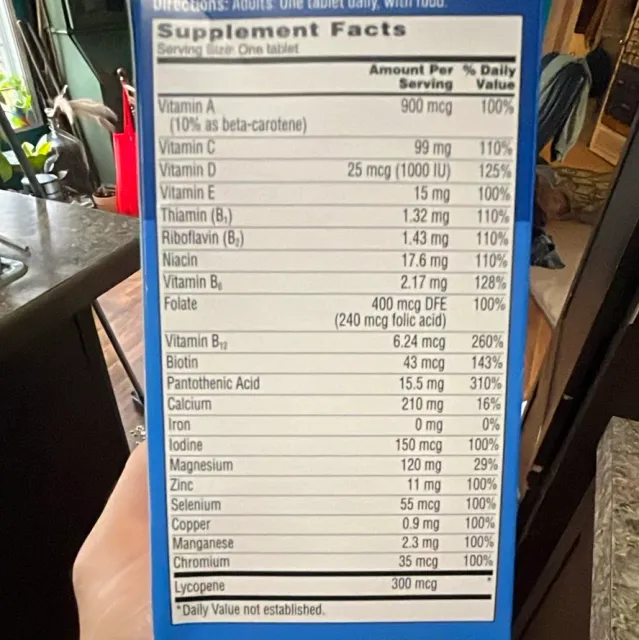
This multivitamin provides a comprehensive blend of essential vitamins at doses aligned with recommended dietary allowances and evidence-based clinical ranges. Vitamin D, B12, and folate are included at levels shown to support immune, neurological, and cardiovascular health, particularly in at-risk populations.