Overview
Vitamin B1 (thiamine) is an essential water-soluble vitamin involved in energy metabolism, particularly in glucose utilization and nerve function. It acts as a coenzyme in the citric acid cycle and is critical for normal neurological function. Thiamine deficiency can lead to serious conditions such as beriberi and Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, particularly in individuals with poor nutrition, alcohol use disorder, or malabsorption. Emerging evidence suggests potential benefits of thiamine supplementation in specific clinical contexts. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial found that adjuvant thiamine (100 mg/day) significantly improved depressive symptoms in patients with major depressive disorder when added to standard SSRI therapy [1]. Other studies have explored B-vitamin combinations, including thiamine, in critically ill patients and those with elevated homocysteine, though effects specific to B1 were not isolated in several trials [2][3]. While thiamine's role in cognitive and cardiovascular health via homocysteine modulation is less clear, it remains crucial for metabolic and neurological health.
Dosage Guide
Recommended Daily Allowance
For generally healthy individuals
Therapeutic Doses
For treatment of specific conditions
Upper Intake Limit
Maximum safe daily intake
Not established mg— No tolerable upper intake level set by the Institute of Medicine due to low toxicity
Special Forms
Alternative forms for specific needs
Common supplemental form, stable, used in fortification
Injectable and oral form, used in clinical settings
Fat-soluble derivative with higher bioavailability; used for diabetic neuropathy and oxidative stress
Clinical Notes
- High-dose thiamine is generally safe but parenteral forms require medical supervision.
- In alcohol use disorder, thiamine should be administered before glucose to prevent precipitating Wernicke's encephalopathy.
- Benfotiamine may be preferred in neuropathic conditions due to superior tissue penetration.
- Monitor for deficiency in malabsorption syndromes, bariatric surgery patients, and chronic diuretic use.
Research
Adjuvant thiamine (100 mg/day) significantly improved depression scores in patients with major depressive disorder over 8 weeks compared to placebo.
A nutritional supplement containing 1.4 mg thiamine daily reduced plasma homocysteine in acutely ill older patients, though effect size was modest.
Low-dose B-complex supplementation (including 10 mg thiamine) had no significant effect on clinical or biochemical outcomes in critically ill COVID-19 patients.
Thiamine levels increased with daily B-complex supplementation (approximately 2.5x RDA) in healthy adults, showing good bioavailability over 6 weeks.
Systematic review found no clear cognitive benefit from B6, B12, or folic acid supplementation; B1-specific effects were not reported.
B-vitamin supplementation (including B1 in combination) did not improve cognitive function in individuals with or without baseline cognitive impairment.
Folic acid and B6/B12 supplementation did not significantly reduce homocysteine or migraine frequency; thiamine was not included.
Homocysteine-lowering with B vitamins did not reduce cardiovascular events in high-risk populations; thiamine not a primary intervention.
Products Containing Vitamin B1(7 reports)

Ortho B Complex is a high-potency B-complex supplement delivering 50 mg each of vitamins B1, B2, B3, B5, and B6, along with 200 mcg B12, 1,360 mcg folic acid (B9), 75 mcg biotin, 19 mg choline, and 50 mg inositol. The formulation emphasizes pharmacological doses of B vitamins, particularly those involved in energy metabolism, homocysteine regulation, and neurological function.

BioActive Complete B-Complex is a high-potency B-vitamin supplement designed to support energy metabolism, neurological function, and homocysteine regulation. The formulation features all eight B vitamins at doses that meet or exceed clinically studied levels for key indications, with particular emphasis on B1, B2, B3, B6, B9, and B12 for metabolic and neurological support.

Anti-Alcohol Complex is a dietary supplement formulated to support liver health, antioxidant defense, and metabolic recovery in individuals with alcohol use or exposure. The formula features high-dose N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) and benfotiamine as primary ingredients, both of which are clinically studied for mitigating alcohol-related oxidative stress and thiamine deficiency. These are supported by antioxidants like vitamin C, selenium, and glutathione precursors to enhance detoxification and cellular protection.
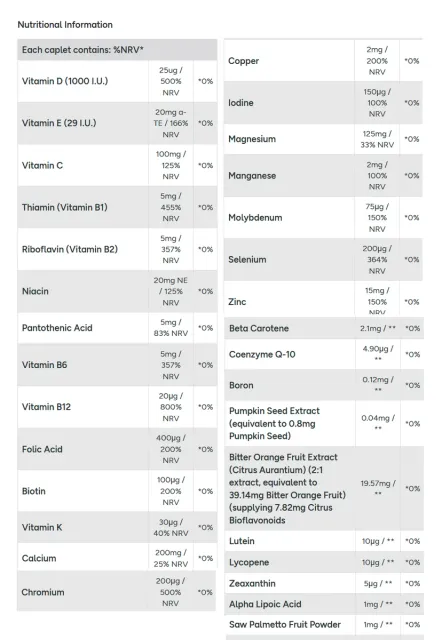
This supplement delivers high-dose vitamin D (25µg/1000 IU) as a primary ingredient, supported by a full B-complex, vitamins C and E. The formulation is designed to support immune function, metabolic health, and antioxidant defense, with clinically relevant dosing of key micronutrients.

HYDROXYCUT HARDCORE LIQUID HEAT is a thermogenic weight management supplement with caffeine and cayenne pepper extract as its primary active ingredients. These compounds are clinically shown to enhance metabolic rate, reduce energy intake, and support fat oxidation. The formulation includes supporting doses of B-vitamins and green coffee bean extract to complement energy metabolism and cardiovascular health.

This testosterone booster contains Rhodiola extract as its primary ingredient, dosed at 385 mg per serving, which aligns closely with clinical doses studied for adaptogenic and fatigue-reducing effects. While Rhodiola may support hormonal balance under stress, there is no direct high-quality evidence that it significantly increases testosterone in humans. Supporting ingredients include thiamin, sodium, ginkgo, and boron, though most are present in sub-clinical or non-targeted amounts for testosterone enhancement.
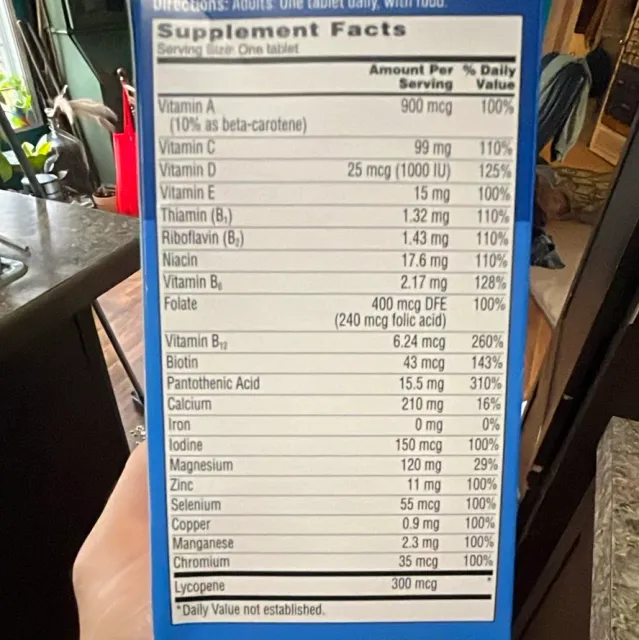
This multivitamin provides a comprehensive blend of essential vitamins at doses aligned with recommended dietary allowances and evidence-based clinical ranges. Vitamin D, B12, and folate are included at levels shown to support immune, neurological, and cardiovascular health, particularly in at-risk populations.