Overview
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant that exists in eight forms, including four tocopherols (alpha-, beta-, gamma-, delta-) and four tocotrienols. Alpha-tocopherol is the primary form in humans and has the highest bioavailability, traditionally recognized for its role in protecting cell membranes from oxidative damage. While early studies suggested potential benefits in cancer and cardiovascular disease prevention due to its antioxidant properties, large-scale clinical trials with high-dose alpha-tocopherol supplementation have largely failed to show protective effects [1][2][4]. Notably, high-dose alpha-tocopherol supplementation may reduce plasma levels of gamma-tocopherol, a form with strong anti-inflammatory and potentially superior cancer-preventive activity [1][2][3]. Emerging evidence highlights the unique health benefits of gamma-tocopherol and tocotrienols, which exhibit neuroprotective, anti-cancer, and cholesterol-lowering effects not seen with alpha-tocopherol [7][6]. Additionally, short-term high-dose alpha-tocopherol (1,200 IU/day) combined with vitamin C may enhance UVB photoprotection [5]. Overall, the form and balance of vitamin E isomers may be critical for health outcomes.
Dosage Guide
Recommended Daily Allowance
For generally healthy individuals
Therapeutic Doses
For treatment of specific conditions
Upper Intake Limit
Maximum safe daily intake
1000 mg— Applies to supplemental forms of alpha-tocopherol; higher risk of hemorrhage at high doses
Special Forms
Alternative forms for specific needs
Provides gamma- and delta-tocopherols; may preserve anti-inflammatory benefits and avoid gamma-tocopherol depletion
Emerging use for neuroprotection, cholesterol reduction, and cancer prevention; not effective for correcting classic vitamin E deficiency
Clinical Notes
- High-dose alpha-tocopherol supplementation (>400 IU/day) may increase risk of hemorrhagic stroke and should be used cautiously with anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin).
- Alpha-tocopherol supplements can lower plasma gamma-tocopherol levels, potentially reducing anti-inflammatory benefits.
- Natural form (d-alpha-tocopherol) is more bioavailable than synthetic (dl-alpha-tocopherol).
- Tocotrienol supplements do not correct vitamin E deficiency as they are poorly retained in the body compared to alpha-tocopherol.
- Monitor for bleeding symptoms when used in high doses or with antiplatelet drugs.
Research
Gamma-tocopherol may be more effective than alpha-tocopherol in cancer prevention due to anti-inflammatory properties; high-dose alpha-tocopherol depletes delta- and gamma-tocopherols.
Alpha-tocopherol supplementation lowers gamma-tocopherol levels; gamma-tocopherol has potent anti-inflammatory activity and is inversely linked to cardiovascular disease.
Alpha-tocopherol shows limited cancer prevention in well-nourished populations; gamma- and delta-tocopherols and tocotrienols show greater promise in preclinical models.
Alpha-tocopherol reduces lipid peroxidation and inflammation in humans, but clinical trials for heart disease prevention have been largely negative.
Oral d-alpha-tocopherol (1,200 IU/day) increases minimal erythema dose, indicating improved UVB protection, especially when combined with vitamin C.
Tocotrienols have neuroprotective, anti-cancer, and cholesterol-lowering effects not observed with tocopherols, warranting further clinical study.
Gamma-tocopherol is the major dietary form in the U.S. and has potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties; human studies are needed to confirm cardiovascular and cancer benefits.
Gamma-tocopherol may be more effective than alpha-tocopherol in reducing oxidation of VLDL, LDL, and HDL in ex vivo models, suggesting a potential advantage in cardiovascular health.
Products Containing Vitamin E(5 reports)

Anti-Alcohol Complex is a dietary supplement formulated to support liver health, antioxidant defense, and metabolic recovery in individuals with alcohol use or exposure. The formula features high-dose N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) and benfotiamine as primary ingredients, both of which are clinically studied for mitigating alcohol-related oxidative stress and thiamine deficiency. These are supported by antioxidants like vitamin C, selenium, and glutathione precursors to enhance detoxification and cellular protection.
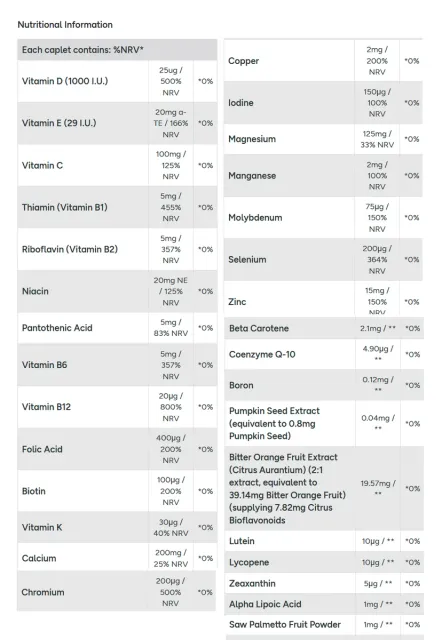
This supplement delivers high-dose vitamin D (25µg/1000 IU) as a primary ingredient, supported by a full B-complex, vitamins C and E. The formulation is designed to support immune function, metabolic health, and antioxidant defense, with clinically relevant dosing of key micronutrients.

This multivitamin formulation delivers essential vitamins at moderate doses, with vitamin D3, vitamin A, and B-complex vitamins as primary contributors to nutritional support. The inclusion of clinically relevant forms such as D3 (cholecalciferol) and methylfolate-capable dosing suggests a focus on bioavailability and metabolic utility.
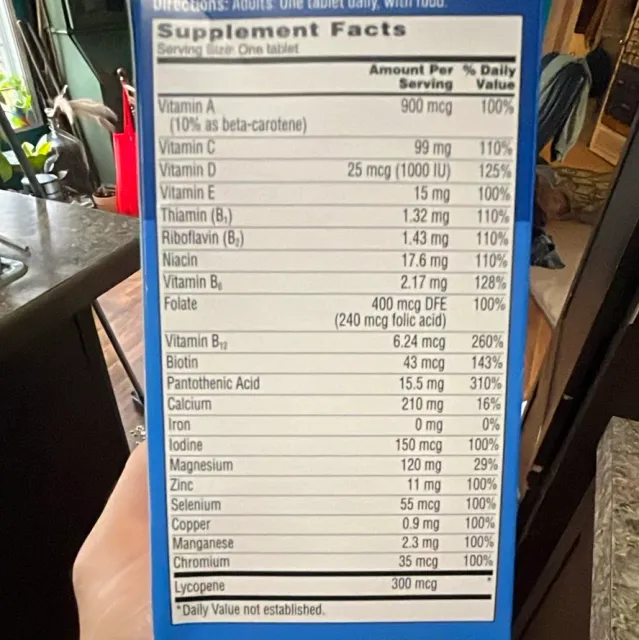
This multivitamin provides a comprehensive blend of essential vitamins at doses aligned with recommended dietary allowances and evidence-based clinical ranges. Vitamin D, B12, and folate are included at levels shown to support immune, neurological, and cardiovascular health, particularly in at-risk populations.

This multivitamin supplement from Nestlé provides clinically relevant doses of vitamin D and calcium as primary nutrients, supporting bone and immune health. Vitamin D (12 mcg) aligns with therapeutic dosing for insufficiency, while calcium (350 mg) contributes meaningfully to daily requirements. Other vitamins and minerals are included at supportive levels, enhancing overall micronutrient intake without targeting specific deficiencies.